External wall and façade elements made of steel have become increasingly popular as architectural design elements in recent decades. Flat exterior wall and façade systems are available in variants with evenly distributed porosity, regular gap widths or even with individual perforations. In addition to the flat systems, lamellar facades are also becoming increasingly common in today’s architecture. In both cases, planners often do not have sufficient load models available for wind and ice loads. In individual cases, there have already been cases of damage caused by insufficient treatment of the wind load effects or the associated stresses.
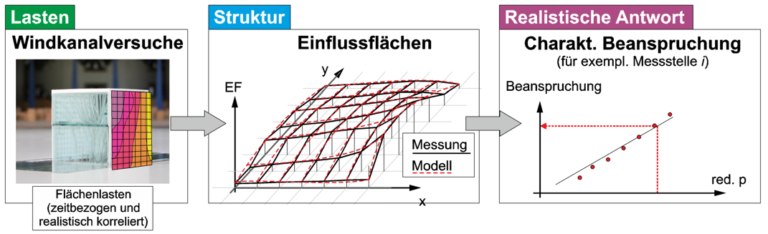
On the basis of extensive wind tunnel tests, the results of which are partly combined with real-scale component tests, this project aims to obtain improved load recommendations for steel facade elements. With regard to the icing of facade elements, a statistical analysis of meteorological data in Germany will be carried out to determine the maximum wind speeds to be expected in the event of component icing. A combination coefficient to be associated with this has not yet been determined for Germany.
The benefits for SMEs after the project has been carried out are thus an improvement in planning security, an increase in the attractiveness of the construction method as a whole, an enlargement of the design scope and an improvement in resource efficiency. It is expected that the use of steel facade elements can thus be increased in the future.
A design aid is being prepared which is aimed at planners working in practice. It contains tabulated and graphically prepared results of the tests and the correspondingly formulated load recommendations.
Forschungsförderung: AiF – Arbeitsgemeinschaft industrieller Forschungsvereinigungen
Partner: Lehr- und Forschungsgebiet Nachhaltigkeit im Metallleichtbau (MLB)
Laufzeit: 03/2019 – 02/2021
Presenation of results (in German):
